At Sweet Fern Studio, I make full use of the many tools our medicine has to offer.
acupuncture
shonishin
Acupuncture is the most well-known technique from Traditional East Asian Medicine. Your body's energy or Qi (pronounced 'chee') runs through your body's organs and channels, and when blockages arise, you feel pain and disharmony. Fine, solid, stainless steel needles are inserted in selected points along those channels on the limbs, torso, back and head to nourish and move your Qi. Acupuncture gives rise to sensations of warmth, lightness, and heaviness throughout the body, and sometimes dull or strong sensation at the location of the needle, but rarely the pain that many associate with needles. After needles are inserted, you will rest for 30-40 minutes, and find you feel extraordinarily relaxed and even fall asleep!
Shonishin is a Japanese non-insertive method of treating infants and children under 10 years old. Small metal tools, brush, tap, and stimulate points on the skin for powerful and pain-free treatment. It is usually soothing and even fun for the child! Following Japanese tradition, Full Moon Shonishin clinics provide well-child care that catalyzes the body to correct imbalances before diseases arise. Shonishin can also treat many childhood physical, emotional and behavioral conditions. Children's courses of treatment are usually shorter than adults', and even the treatments themselves are short, usually just 20-30 minutes.
moxibustion
Moxibusion or "Moxa" involves burning a dried herb, artemisia vulgaris, or mugwort, over a specific acupuncture point, or in a region. Moxa can be placed on the top of the needle or directly on the skin to send penetrating warmth directly into an acupuncture point. It is also compressed into different-sized sticks and can be burned near a point, or in a metal tool called 'tigerthermy' which gently glides along the skin to disperse warmth along sensitive skin. I use caution, experience and good communication to reduce the risk of burns.
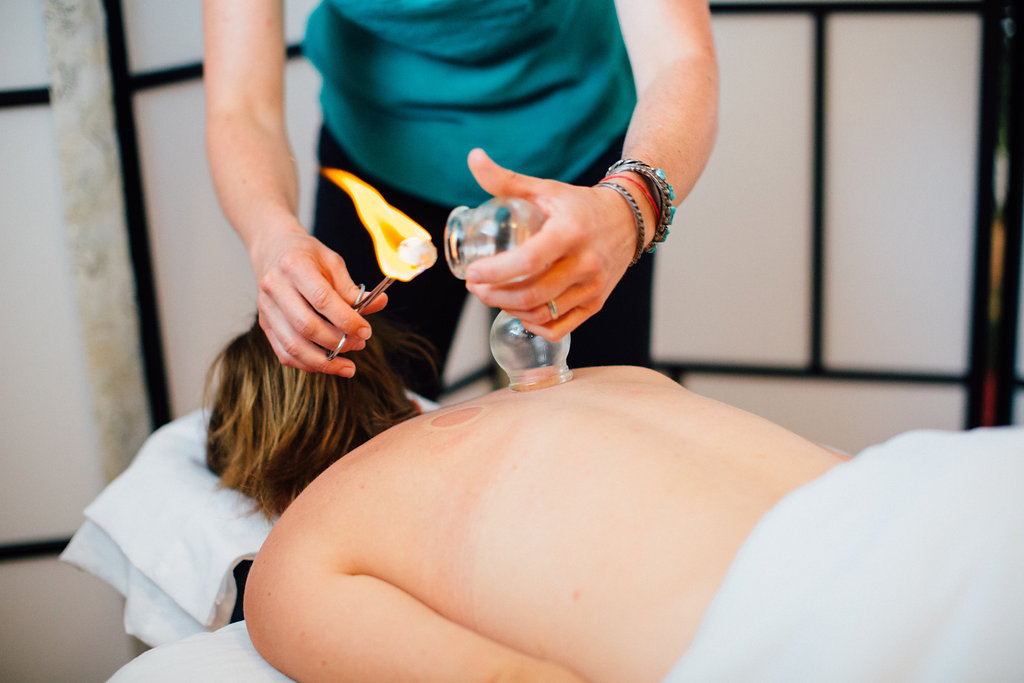
cupping
tui-na
Cupping is a traditional practice found in many cultures where glass suction cups are placed on the skin, pulling up the skin and fascia to facilitate the body's natural detoxification and circulation processes. Once placed, they may either remain in place for a few minutes, or be used with oil to slide over the skin surface. Cupping feels great on tight muscles, and draws out sharp pain from injuries. Consider it for those early signs of cold symptoms (stiff neck, chills, slight sore throat) or to loosen up chronic lung congestion. It may be used in addition to acupuncture at no extra cost.
Tui-na is a massage form that uses the hands to treat the points and channels of Chinese medicine. There are techniques that are similar to the Western experience of a massage - it is usually relaxing, and good for musculo-skeletal issues like pain and injuries. However, other elements are unique: often treatment is applied through clothes or a sheet, and some movements are more vigorous than a slow, Swedish massage. There are also specific tui-na treatments for a wide range of children's disorders, making this massage form highly useful in the clinic and at home.
herbal medicine, diet & lifestyle
Chinese Herbal Medicine commonly uses approximately 400 'herbs', most of which are plants (seeds, fruits, barks, twigs, grasses, roots and rhizomes), although there are also animal and mineral products in the pharmacopeia. (Please let me know if you avoid using animal products!) Many of the plants grow and are widely used all over the world, so what makes the tradition Chinese Herbal Medicine is how the herbs are categorized by their function in the body, and are carefully selected to work together to effect a desired change. In contrast to Western herbs, which are often used alone, Chinese herbs are typically combined into customized formulas administered in tea, powder, or capsule form.
Diet therapy helps you choose foods that are best for your body in the current time and place. Whereas a Western meal would be analyzed by its components of proteins, grains, vegetables, fruits, etc., Chinese dietetics constructs a balanced meal based on the flavors and natures (cooling to warming) of the foods. Each property plays an important role in the body, and each person's constitution and condition benefits from different combinations of flavors, temperatures, and preparation methods.